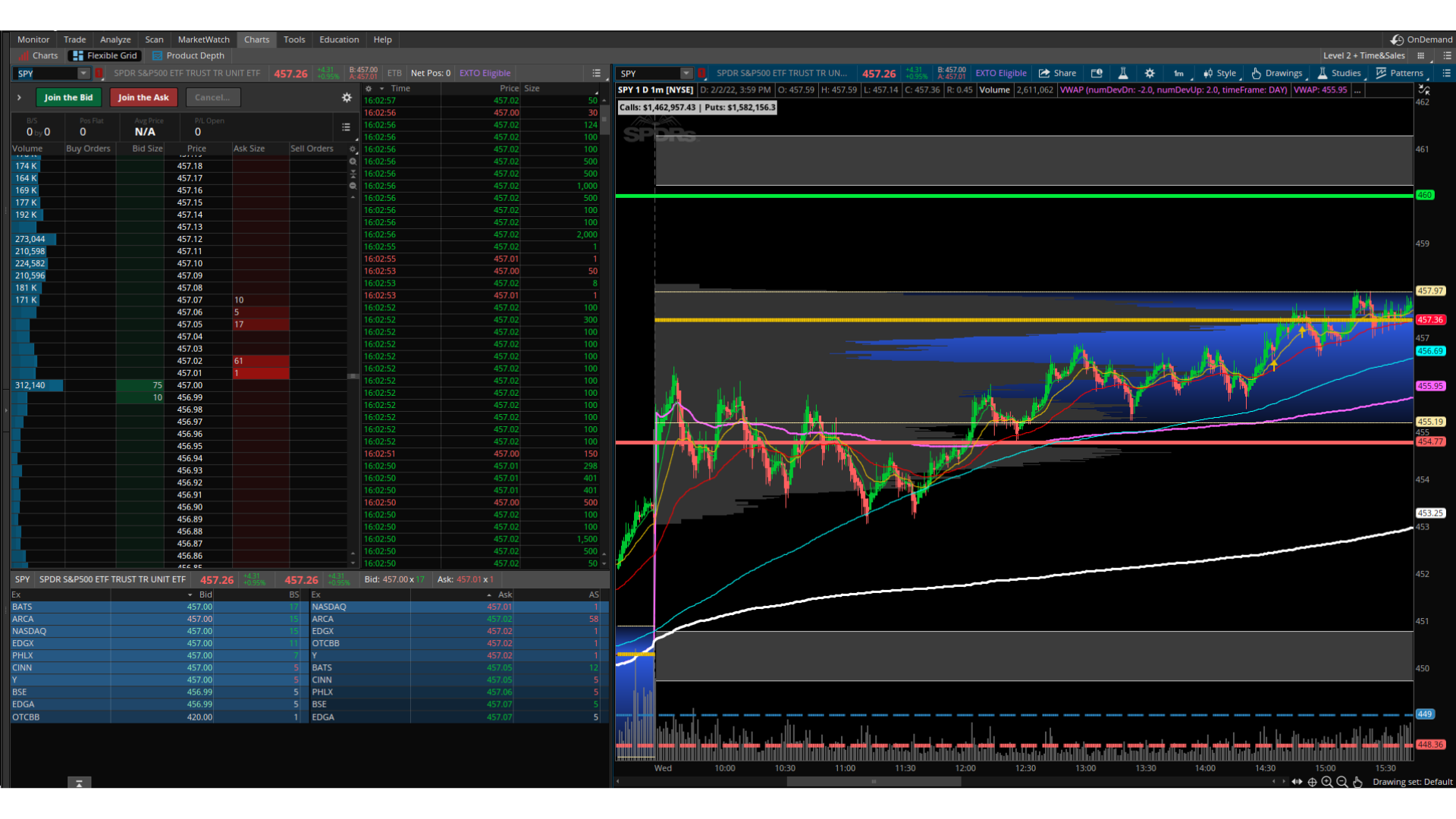
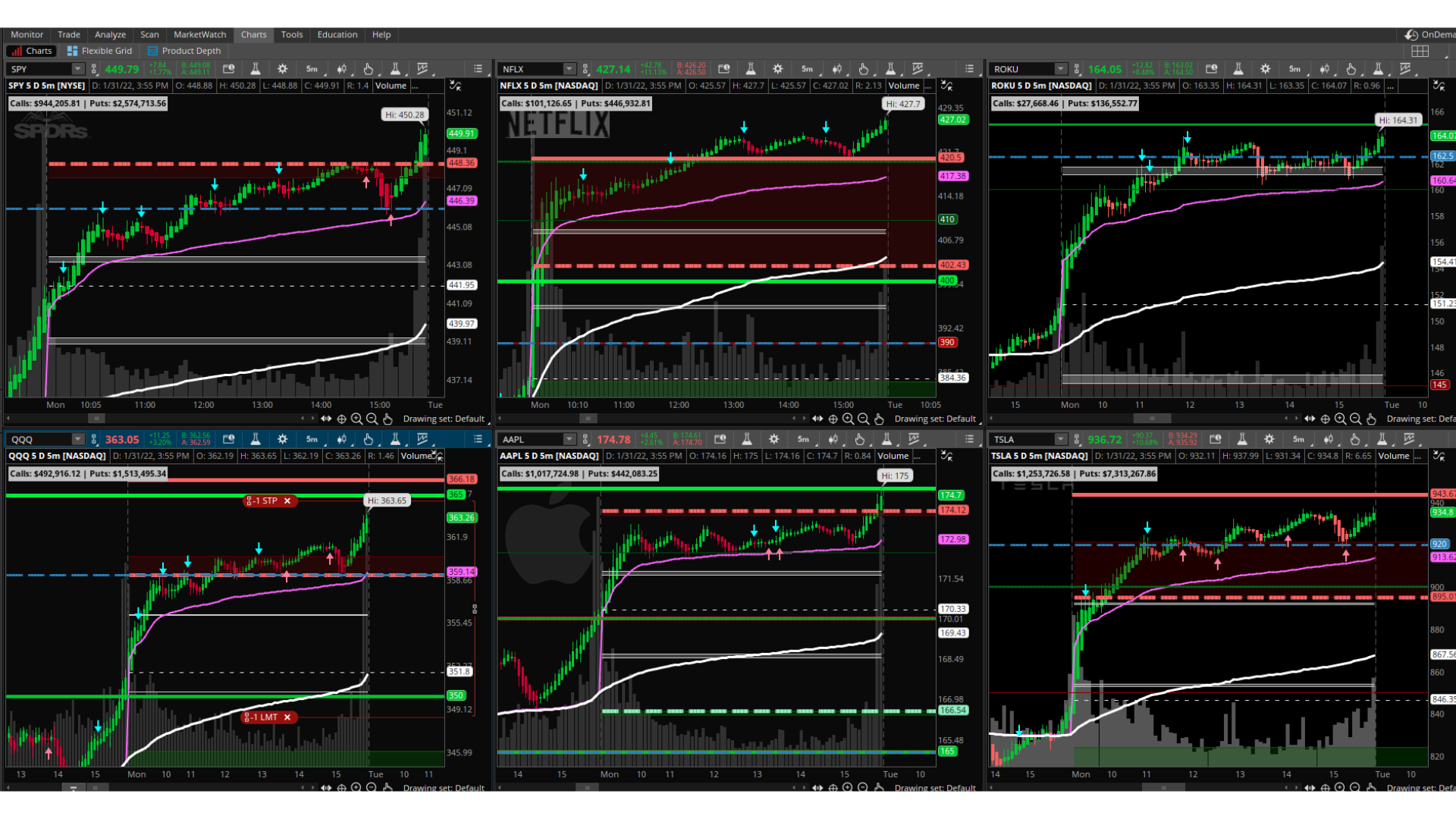
20 Minute Trader Master Class
Options Trading Guide
Trading options is not for beginners. Learn what’s required to get going.
Options trading may initially seem complicated, but if you understand a few fundamental concepts, it becomes clear. Investor portfolios are frequently built using a variety of asset classes. Stocks, bonds, ETFs, and even mutual funds could be among them.
Another asset type is options, and when used properly, they can provide many benefits beyond what trading stocks and ETFs alone can.
Key Takeaways
- A contract known as an option grants the buyer the right, but not the responsibility, to buy (in the case of a call) or sell (in the case of a put) the underlying asset at a certain price on or before a specific date.
- While options can be on any underlying asset, including bonds, currencies, and commodities, a stock option contract typically represents 100 shares of the underlying stock.
- Options are called “derivatives” because they get their value from an underlying asset.
- Options are used by people to generate money, speculate, and manage risk.
What Are Options?
Options are contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the duty, to purchase or sell a certain quantity of the underlying asset at a specified price on or before the contract’s expiration date. Options, like most other investments, can be bought with a brokerage account.
In addition to boosting, one’s portfolio, options are extremely effective. They achieve this by gaining more money, security, and even bargaining power. An investor’s objective should inform the choice of an option scenario. Popularly, options are used to reduce losses in the event of a decline in the stock market. Options, in reality, were originally developed for risk management and protection. Option hedging’s main goal is to lessen exposure to danger while keeping costs manageable. A good analogy would be an insurance policy, which is how we may conceive of alternatives here. Options can be used to protect investments from a market decline, just like homeowners’ and auto insurance.
Let’s say you’re interested in purchasing technology stocks but are wary of taking on too much risk. You may protect yourself from losses while profiting from gains by purchasing put options. During a short squeeze, in particular, call options can be utilized to mitigate losses for short sellers should the underlying price move against their transaction.
Contract options can be utilized for both hedging and speculation. To speculate is to make a bet on the likely movement of prices. A speculator may believe, based on fundamental or technical analysis, that the price of a stock will rise in the near future. Investors who are gambling could either purchase shares or call options. Some investors prefer to utilize call options as a tool for speculation rather than purchasing shares of stock outright because of the leverage they provide. A call option that is far out of the money may cost only a few dollars, or even cents, while a share of stock that is worth $100 would cost the investor the entire $100.
A Practical Explanation of How Options Operate:
Estimating the likelihood of a series of price changes is the crux of option contract valuation. An option’s price typically rises as the likelihood of its underlying event increases. A call option’s value, for instance, rises as the underlying stock price rises. The relative worth of options can only be grasped by knowing this.
The value of an option decreases as its remaining time to expiration approaches zero. This is because, as time nears expiration, the likelihood of a price change in the underlying stock decreases. Because of this, options are a poor investment. An out-of-the-money one-month option loses value every day if the underlying stock doesn’t move during that time. A one-month option will be worth less than a three-month option due to the time value of money. This is due to the fact that if you have more time on your hands, the price is more likely to move in your favor, and vice versa.
A one-month expiration on the same option strike will cost less than a one-year expiration on the same strike. Time decay is responsible for options’ wasting nature. Even if there is no change in the stock price, the value of your option will decrease from today to tomorrow.
Additionally, option prices rise as volatility rises. This is because the odds of an outcome increase as uncertainty grows. The likelihood of large price changes in either direction increases as the volatility of the underlying asset rises. The likelihood of something happening grows as its price fluctuates more widely. As a result, option prices tend to rise as volatility increases. This is why options trading and volatility go hand in hand.
To find out how much the call option will cost in total, multiply the contract premium by 100. In the United States, a typical stock option contract gives the buyer the right to buy 100 shares.
The vast majority of holders decide to cash in their gains by selling their holdings. This means that in order to close the position, the writer must buy back options from option holders in the market. About 10% of options are actually put to use, 60% are closed out through trading, and 30% simply expire with no value.
Option types include Calls and Puts
One type of derivative security is options. Options are considered derivatives because their value is derived from that of another asset. If you purchase an options contract, you have the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price by a certain date if you purchase an options contract. The holder of a call option has the right to purchase a share of stock, while the holder of a put option has the opposite right. A call option can be compared to saving up money for a future purchase.
Call Options
The owner of a call option has the right but not the obligation to purchase the underlying security at the strike price until the option's expiration. With a rise in the underlying security's price comes an increase in the value of a call option (calls have a positive delta). If you believe the underlying asset's price will rise, you can use a long call as a speculative investment with unlimited upside and limited risk (maximum loss equal to premium).
Put Options
A put option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying stock at the strike price on or before expiration. This is in contrast to a call option, which imposes the obligation to buy the stock at the strike price. Since the value of a long-put increases as the price of the underlying security declines, holding one constitutes a short position in the underlying security (they have a negative delta). In order to protect their investments, investors can buy protective puts as a form of insurance.
The Master Class in Trading:
What is In It?
✓ STOCK MARKET FOR DUMMIES
✓ OPTIONS FOR DUMMIES
✓ SIMPLE DEFINITIONS….FOR DUMMIES
✓ THE RECIPE FOR PATTERN DISCOVERY
✓ GRAPHS ORIENTATION. Okay, okay…for dummies.
✓ OVERPAID CHAT-BOX COACHES… Yeah, we beefed up the premium customer service with real people trained on the 20-Minute Trader® system. Just hit the chat box and get ACTUAL expert assistance.
✓ 28 LESSONS
✓ 3.5 HOURS OF VIDEO CONTENT